All products featured are independently chosen by us. However, SoundGuys may receive a commission on orders placed through its retail links. See our ethics statement.
Can you test your hearing online for free?
May 9, 2022
Hearing loss is one of the downsides of aging, and it increasingly affects young people. Drowning out the world with loud music, immersing yourself in a video game with your headphones on for hours on end, or rocking out in the first row right next to the speakers—we’ve all done it, some starting at a very young age.
Repetitive exposure to loud sounds can cause irreversible noise-induced hearing loss. In fact, one in eight people in the US aged 12 years or older has hearing loss. If you’re wondering whether you’re one of them, there’s an easy way to find out. Online hearing tests are free, quick, and can reveal hearing loss that may affect speech recognition.
Editor’s note: this article was updated on May 9, 2022, to include the WHO’s hearing test.
What does a standard hearing test do?
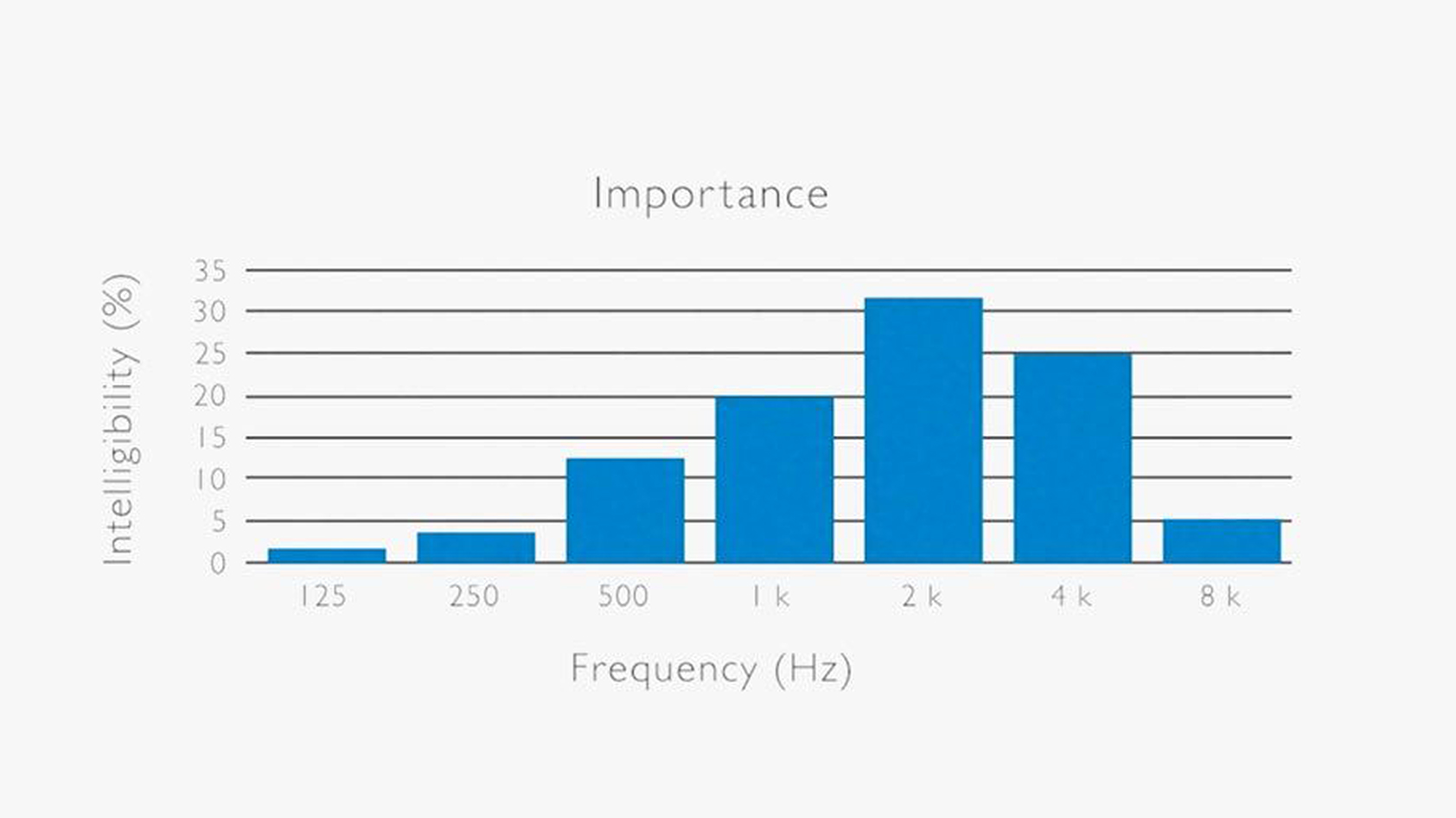
The purpose of a hearing test is to find out whether you can still hear and understand what other people say. Hence, although humans can technically hear frequencies between 20-20,000Hz, hearing tests and hearing aids generally only cover frequencies from 125-8,000Hz. This frequency range corresponds to the range critical for speech intelligibility.
In a comprehensive hearing test, an audiologist will test your ability to hear sounds using professional equipment and a series of tests:
- Pure tone audiometry: You wear headphones and push a button or otherwise signal when you hear a sound at different frequencies, measured in Hertz (Hz), and volumes, measured in decibels (dB). Also known as an air conduction test, this can reveal damage to the middle ear, including the eardrum and the small bones that transform sound waves into mechanical energy.
- Bone conduction: Instead of headphones, you wear a small device behind your ears that emits vibrations picked up directly by the cochlea in your inner ear. As with the previous test, you signal when you hear a sound. This test bypasses the middle ear and can help the audiologist pinpoint the source of the hearing loss.
- Auditory brainstem response: This is an advanced test for babies, children, or individuals with potential hearing loss in the brain pathway. The patient wears headphones and electrodes attached to the skin of their head. A computer records brain waves captured by the electrodes. If the inner ear and the brain pathway work, the brain waves will change in response to sound. No interaction from the patient is required.
- Speech recognition: You’ll wear headphones and listen to words played back at different volumes and with or without background noise. You’ll repeat each word to the best of your abilities. This test can expose hidden hearing loss, which is when you can hear everything, but struggle to understand speech.
- Otoacoustic emissions: The audiologist will place a probe with a microphone and speaker in your ear canal. As the speaker emits sounds, the hair cells of the inner ear should vibrate and produce faint sounds called otoacoustic emissions that the microphone can pick up. A lack of otoacoustic emissions from the inner ear’s hair cells indicates hearing loss that exceeds 25-30dB.
The results indicate how well you can hear and which parts of your ear, if any, are damaged. An audiogram offers a visual representation of the frequencies you can hear and at which volumes.
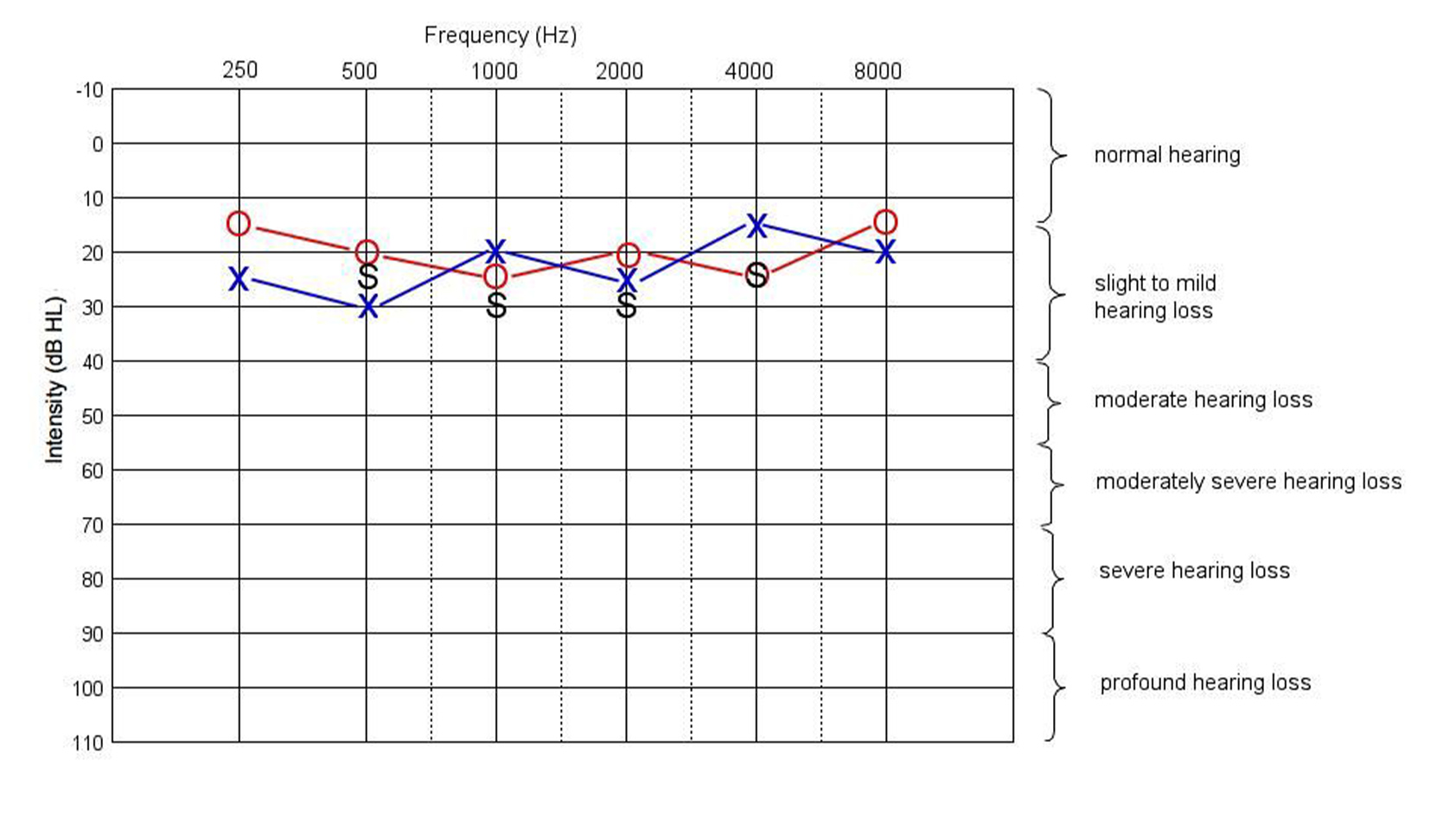
People with hearing loss of 10dB or more, for example, struggle to hear rustling leaves and birds chirping. At more than 20dB, dripping water or whispers become inaudible. Most sounds relevant to speech are clustered in a decibel range known as the speech banana.
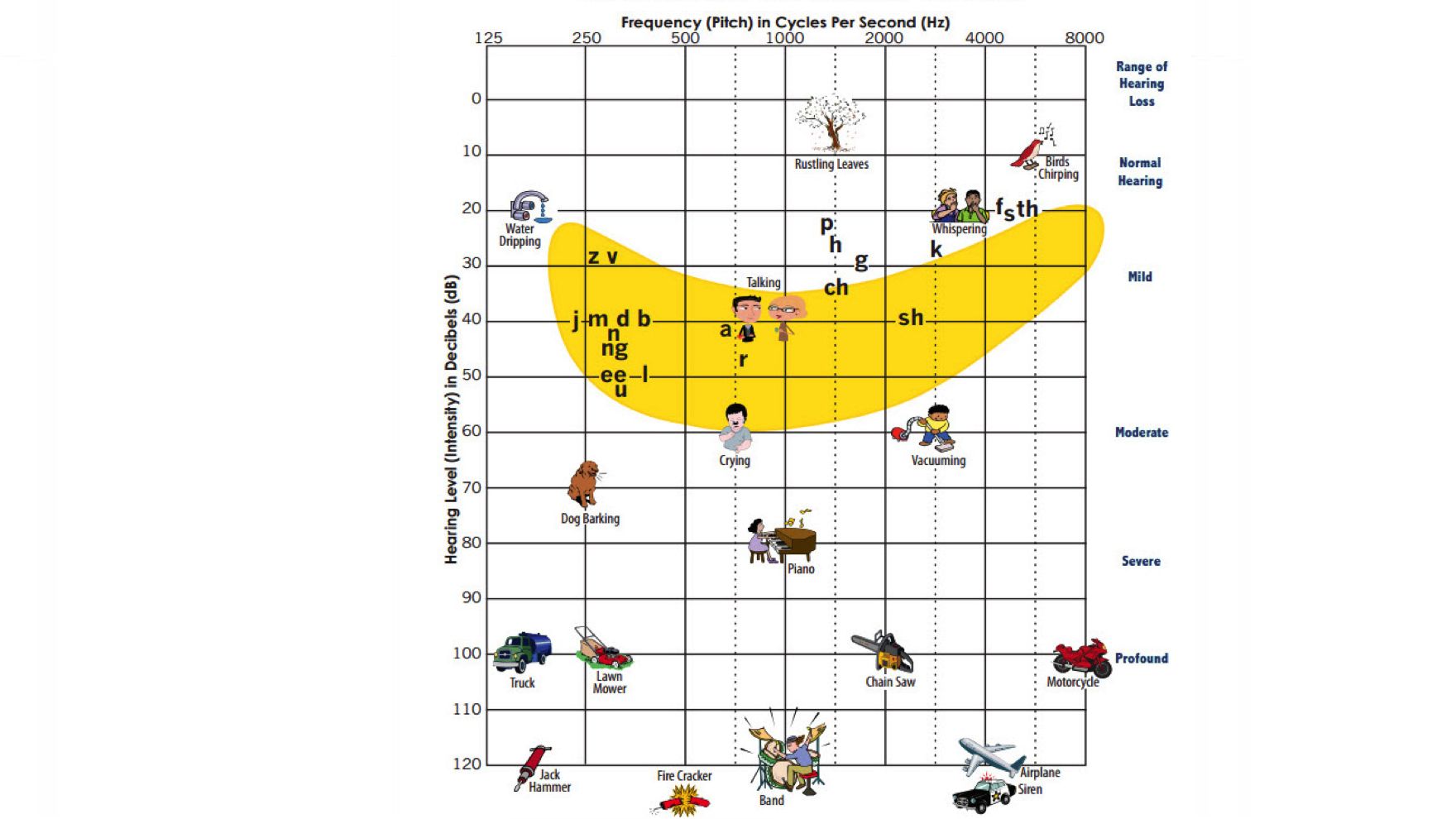
When hearing loss affects speech recognition, a hearing aid is inevitable. However, even in milder cases early treatment can slow down hearing loss and prevent cognitive decline, which is commonly correlated with hearing loss. If you’re not ready to see a doctor, you can try an online hearing test first.
How do online hearing tests compare?
Free online hearing tests can give you a rough idea of whether or not your declining hearing requires medical attention.
Depending on the test you choose, you’ll do either a simplified pure tone audiometry or a speech recognition test, or both. Most tests also feature questions that can uncover hidden hearing loss. While some tests probe each ear individually, others don’t distinguish between the left and right ear.
Before you take a free online hearing test, here’s how to prepare:
- Pick your best headphones, ideally over-ear.
- Connect them to your phone, laptop, or desktop computer.
- Set yourself up in a quiet place or reduce external noise as much as possible. You may need to close the door, windows, and temporarily turn off loud devices like an A/C unit or heater.
Below is an overview of the best online hearing tests. We’ve included tests that collect personal information or contact data only if they offered a worthwhile benefit.
| Name | Contact data | Setup | Duration | Test scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones or speakers | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones | Duration 3 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name Shoebox (also used by Widex and Rexton) | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data Email address | Setup Headphones | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data Name Email address Phone number | Setup Headphones | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data Name Email address Phone number | Setup Headphones | Duration 5-15 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones or Speakers | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones | Duration 2 minutes | Test scope
|
| Name | Contact data None needed | Setup Headphones | Duration 5 minutes | Test scope
|
Online tests can’t replace a professional hearing test because they don’t include a diagnosis, nor can they prescribe treatment.
When should you seek medical advice?
When an online test reveals that you have hearing loss, you should immediately seek medical advice. We all lose some hearing as we age, but it gets serious when it starts to affect frequencies below 8,000Hz because the hearing loss has started eating into the speech frequency range. The sooner you know what’s causing your hearing loss, the sooner you can take steps to protect your hearing and retain more of it in the long run. Hearing loss usually isn’t reversible, but in some cases, you can slow it down.
What’s more, hearing loss is a precursor to dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and cognitive decline in general. Whether it’s causation or correlation, treatment such as wearing a hearing aid can protect your mental health and improve your quality of life.